All input and output files can be downloaded here.
Geometry Optimization
Geometry optimization intends to find a minimum on the potential energy surface from a starting geometry. All energy calculation methods, including quantum mechanics (QM), molecular mechanics (MM), and QM/MM, can be used for geometry optimization, as long as you change energy to opt in the input files.
Three Optimizations
QM Geometry Optimization
For water in Density Functional Theory Calculations, the geometry optimization is:
basis
def2-tzvp
end
scf
charge 0
spin2p1 1
type R
end
grimmedisp
type bj
end
mol
O 0. 0.00000000 -0.11081188
H 0. -0.78397589 0.44324751
H 0. 0.78397589 0.44324751
end
task
opt b3lyp # Just change energy to opt.
endAfter optimization, you will find two additional files:
water-opt.xyzThe last optimized structure. It is updating during the optimization.water-opt-traj.xyzAll intermediate structures during the optimization.
MM Geometry Optimization
The protein example in Molecular Mechanics Energy can be easily changed for geometry optimization:
charmm
parameters par_all36m_prot.prm toppar_water_ions.str
topology step2_solvator.psf
scaling14 1.0
rcutoff 12.0
rswitch 10.0
use_PBC
Lbox 64 64 64
electrostatic pme
PMEk 64 64 64
end
mol
step2_solvator.pdb
end
task
opt charmm
endQM/MM Geometry Optimization
Both examples in Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) Energy can be easily changed for geometry optimization, as long as you change energy to opt. For example:
charmm
parameters par_all36m_prot.prm
topology step1_pdbreader.psf
scaling14 1.0
rcutoff 12.0
rswitch 13.0
end
basis
def2-svp
end
scf
charge 0
spin2p1 1
type R
end
grimmedisp
type bj
end
qmmm
qm_region 779 792-815
end
mol
step1_pdbreader.pdb
end
task
opt b3lyp/charmm
endSome Options
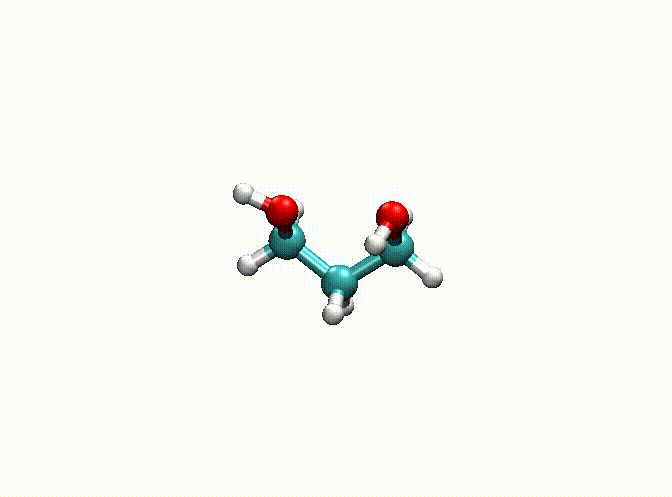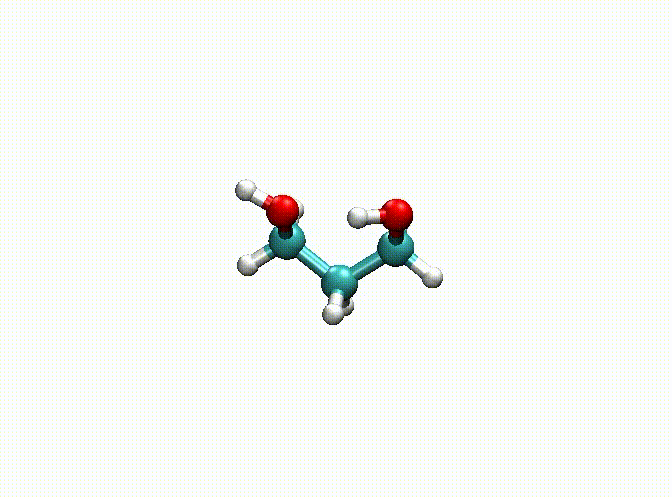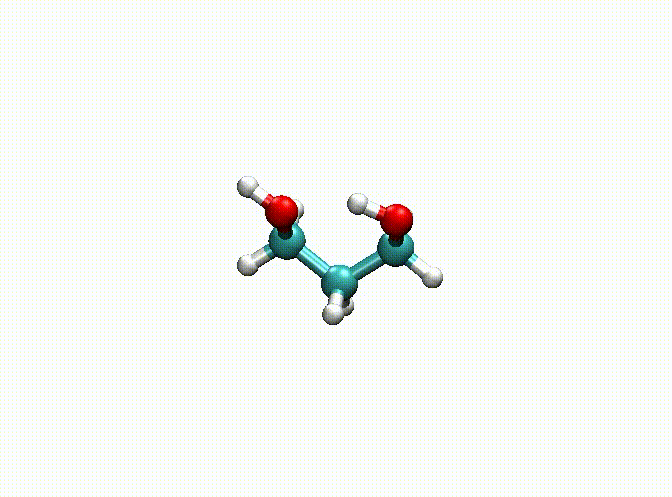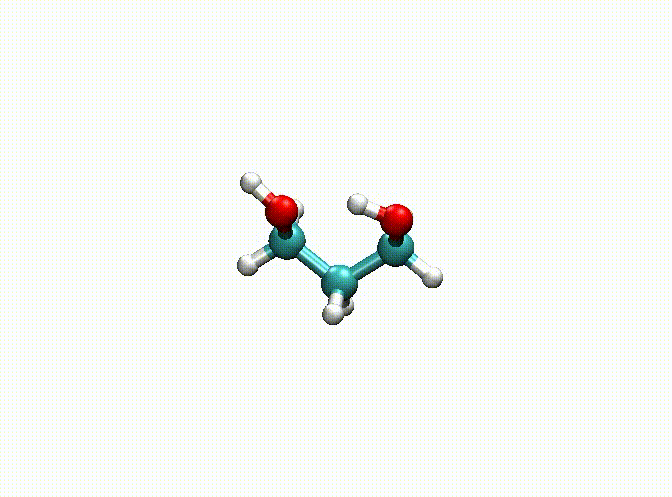
There are some options for geometry optimization. For example, the following example:
basis
def2-svp
end
scf
charge 0
spin2p1 1
type R
end
grimmedisp
type bj
end
opt
num_steps 1000
epsilon 1.E-5
fix 1-9
end
mol
C -4.08368628 0.86864405 0.00000000
H -3.72701344 1.37304224 -0.87365150
H -5.15368628 0.86865724 0.00000000
C -3.57037057 -0.58328810 0.00000000
H -3.92704565 -1.08768708 -0.87365013
H -3.92704123 -1.08768606 0.87365253
C -2.03037057 -0.58330630 -0.00000339
H -1.67371614 -1.59211630 -0.00000091
H -1.67370018 -0.07891023 -0.87365712
O -3.60701136 1.54274631 1.16759033
H -4.11695915 2.34433532 1.30546096
O -1.55369311 0.09080013 1.16758349
H -2.04104440 -0.21550578 1.93587082
end
task
opt b3lyp
endThe geometry optimization control block is opt ... end:
num_stepsThe maximum number of geometry steps. Default is1000.epsilonA convergence label. Usually, you do not need to change it.fixThe atoms that you want to fix during geometry optimization.
In the above example, we fix the alkyl chain and only relax the hydroxyl groups. The final optimization result can be seen in c3h8o2-opt.xyz and c3h8o2-opt-traj.xyz. The animation of the optimization is shown below. Obviously, atoms 1-9 have been fixed.